TECHNICAL HANDBOOK ON BUILDING CONSTRUCTION FOR FIELD ENGINEERS
STRUCTURAL DESIGN – SOIL INVESTIGATION AND FOUNDATION.
 |
| HAND BOOK ON BUILDING CONSTRUCTION |
TO DOWNLOAD THIS BOOK SCROLL DOWN
The structural safety of this design loadsConsequently, the selection of suitable site and soil to bear the election of Site. The first and foremost job in construction is to select a suitable site for the building. A properly selected site of the building gives enhanced beauty to the
The following points should be considered while selecting the site. The soil at the building site should not be of artificially made-up type.
| BOOK TITLE | DOWNLOAD LINK |
| autoCad 2020 autocad book | LINK |
| ESTIMATION PROCEDURE SEPTIC TANK | LINK |
| BASIC CIVIL ENGINEERING BOOK BY BHAVIKATI DOWNLOAD | LINK |
| Water tank design example download pdf | LINK |
| THEORY AND PRACTICE OF PILE FOUNDATION BOOK DOWNLOAD | LINK |
| Staad pro manual download pdf | LINK |
| cement mortar calculation for brickwork and plastering and steel Quantity | LINK |
| Understanding Structural analysis | LINK |
| Illustrated Design of RCC buildings | LINK |
| Calculation of Quantity of material for RCC cement sand aggregate | LINK |
| AGGREMENT COPY BETWEEN CONTRACTOR AND CLIENT | LINK |
| Existing building Stability check procedure | LINK |
settlement and cracks are quite common in such buildings.
A. The site should not be undulating since this leads to an increase in cost for
B. The site should have its general slope, to enable easy drainage.
C. Civic services, such as water supply mains, electric lines, telephone lines, drainage, sewers, should be near the site so that no additional costs
D. The groundwater table on the site should not be high.
E. The selected site should be as far as possible large enough to provide sufficient light and air to the building with drainage facilities and adequate
F. The site should possess good soil at a reasonable depth.is above the plinth level and the substructure, which is below the plinth level. Generally, about 30 per cent of the total construction cost is spent on the
G.Soil is a material produced by the weathering of the solid rock. grained (Gravel, sand), fine-grained (silt and clay) based on the soil type and size as
| PURPOSE | PLAN SIZE | DOWNLOAD LINK |
| RESIDENTIAL | 30' X 60' | LINK |
| RESIDENTIAL | 700 Sq.ft | LINK |
| RESIDENTIAL | 30' X 50' | LINK |
| RESIDENTIAL | 40' X 80' | LINK |
| SCHOOL | 4 CLASS ROOM | LINK |
| STRUCTURAL DRAWING SCHOOL | 4 CLASS ROOM | LINK |
| STRUCTURAL DRAWING RESIDENTIAL | 40' X 80' | LINK |
| AUTOCAD PLAN 30' X 70' | 30' X 70' | LINK |
| AUTOCAD PLAN | 30' X 60' | LINK |
INDUSTRIAL PLAN
| (18m X 38m) | LINK |
As per IS: 1904-1986, the soil is classified into four types
a) rocks,
b) noncohesive soils,
c) cohesive soils and d) made up ground and fills.
are gravel, sand and mixture of sand and gravel, sand and silt and mixed soils. Cohesive soils are hard or stiff clay in dry, medium moisture condition, soft
The soil can be placed in different groups based on the index properties, and the engineering properties such as strength characteristics (shear strength) volume change characteristics or compressibility (settlement) and permeability (rate of settlement).
Field test data are essential to know the exact magnitudes of these values.More often laboratory tests are found to be necessary to cross-check the values. In some other situations where field-testing is not possible, the laboratory test has aBased on the test the ability of a soil mass to support imposed loading is governed by the shear strength of the soil.shearing strength of the soil becomes primarily important in foundation design, highway and airfield design, slope stability problems, and lateral earth pressure problems that deal with the forces exerted on underground walls, retaining walls,
The purpose of this test is to correlate the compactness of granular soil with n’ value from which angle of shearing resistance, values are estimated.conducted with a standard soil exploration device and a split spoon sampler. values corrected for overburden and saturation are used for the estimation of strength been employed for a number of years as a method of indirect evaluation of subsurface soils. This is highly useful for granular cohesionless soil.denseness. ‘N’ value is the standard penetration value. Soil bearing capacity is the maximum load per unit area, which the soil resist
| BOOK TITLE | DOWNLOAD LINK |
| STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS DESIGN MANUAL BOOK | LINK |
| SURVEYING BOOK | LINK |
| STEEL DETAILING MANUAL BOOK | LINK |
| SOIL MECHANICS LABORATORY MANUAL | LINK |
| Fundamentals of Surveying by S.K. Roy | LINK |
| PRINCIPLES OF STRUCTURAL DESIGN BY RAMS. GUPTA | LINK |
| BASIC CIVIL ENGINEERING BOOK | LINK |
| ENGINEERING PLUMBING DESIGN BOOK | LINK |
| TECHNICAL HAND BOOK ON BUILDING CONSTRUCTION FOR FIELD ENGINEERS | LINK |
| ELEMENTARY STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND DESIGN BOOK | LINK |
By dividing the ultimate bearing powers of soil by a
In case if SBC is very low, the
1) Chemical treatments like injecting lime, cement etc.,
The allowable bearing pressure shall be taken as either of the following
2) The safe bearing capacity on the basis of shear strength characteristics of
3) The allowable bearing pressure that the soil can take without exceeding the
Where the engineering properties of the soil are available (ie) cohesion, angle of internal friction, density etc., the bearing capacity of the soil shall be calculated
| PURPOSE | PLAN SIZE | DOWNLOAD LINK |
| RESIDENTIAL | 30' X 60' | LINK |
| RESIDENTIAL | 700 Sq.ft | LINK |
| RESIDENTIAL | 30' X 50' | LINK |
| RESIDENTIAL | 40' X 80' | LINK |
| SCHOOL | 4 CLASS ROOM | LINK |
| STRUCTURAL DRAWING SCHOOL | 4 CLASS ROOM | LINK |
| STRUCTURAL DRAWING RESIDENTIAL | 40' X 80' | LINK |
| AUTOCAD PLAN 30' X 70' | 30' X 70' | LINK |
| AUTOCAD PLAN | 30' X 60' | LINK |
INDUSTRIAL PLAN
| (18m X 38m) | LINK |
The factor of safety of 2.5 shall be adopted for safe.The bearing capacity of the soil is affected by wind and seismic forces.
Loads on Foundations (IS : 875-1987 of Part 6 – section 1 of NBC 2005):
The type of foundation to be used depends upon the loads borne by it. There are various types of loads borne by the foundation – dead load, live load (imposed load), wind load, snow load, seismic load and other external loads.
This is the self-weight of the various components of a building. for the future construction must also be made in the dead load calculation.calculate the dead load, acknowledge of the weight of the common building materials this is also known as superimposed load and is the moveable load on the floor. This includes the weight of persons standing on a floor, weight of material stored temporarily on a floor, weight of snow, etc.
In the case of tall buildings, the effect due to wind should be considered. The exposed sides and roofs of such buildings are subjected to wind pressure and its effect is to reduce the pressure on the foundation in the windward side and to increase.
_________________________________________________________________________________
| BOOK TITLE | DOWNLOAD LINK |
| autoCad 2020 autocad book | LINK |
| ESTIMATION PROCEDURE SEPTIC TANK | LINK |
| BASIC CIVIL ENGINEERING BOOK BY BHAVIKATI DOWNLOAD | LINK |
| Water tank design example download pdf | LINK |
| THEORY AND PRACTICE OF PILE FOUNDATION BOOK DOWNLOAD | LINK |
| Staad pro manual download pdf | LINK |
| cement mortar calculation for brickwork and plastering and steel Quantity | LINK |
| Understanding Structural analysis | LINK |
| Illustrated Design of RCC buildings | LINK |
| Calculation of Quantity of material for RCC cement sand aggregate | LINK |
| AGGREMENT COPY BETWEEN CONTRACTOR AND CLIENT | LINK |
| Existing building Stability check procedure | LINK |





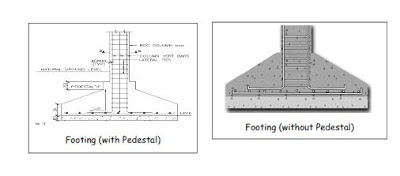








COMMENTS