flat slab design| flat slab reinforcement details | flat slab details
flat slab design| flat slab reinforcement details |flat slab details
INTRODUCTION- FLAT SLAB DESIGN
Flat slabs system of construction is one in which the beams are used in the conventional methods of construction. The slab is directly supported on the column and load from the slab is directly transferred to the columns and to the foundation. To support heavy loads the thickness of the Flat slab near the support with the column is increased to withstand load and these are called drops, or columns are generally provided with enlarged heads called column heads or capitals.
- Column strip
- Middle strip
- Panel
- column head
DESIGN PROCEDURE - FLAT SLAB DESIGN
1. Determine design life
2. Assess actions on the slab
3. Determine which combinations of actions apply
4. Determine loading arrangements
5. Assess durability requirements and determine concrete strength
6. Check cover requirements for appropriate fire resistance period
7. Calculate min. cover for durability, fire and bond requirements
8. Analyse structure to obtain critical moments and shear forces
9. Design flexural reinforcement
10 . Check for deflection
11 .Check punching shear capacity
12 .Check spacing of bars
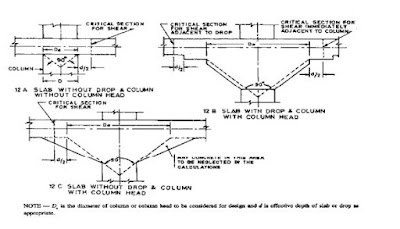
Drop of flat slabs:
Where a drop panel is used to reduce the amount of negative moment reinforcement over the column of a flat slab, the size of the drop panel shall be in accordance with the following:
- Drop panel shall extend in each direction from the centerline of support a distance not less than one-sixth the span length measured from centre-to center of supports in that direction.
- Projection of drop panel below the slab shall be at least one-quarter the slab thickness beyond the drop.
- In computing required slab reinforcement, the thickness of the drop panel below the slab shall not be assumed greater than one-quarter the distance from the edge of the drop panel to the edge of column or column capital
 |
| flat slab design |
DESIGN METHODOLOGY
There must be a minimum of 3 continuous spans in each direction.
- Panels shall be rectangular with a ratio of longer to shorter spans, centre to centre of supports, not greater than 2.Successive span lengths, centre-to-centre of supports, in each direction, shall not differ by more than 1/3 of the longer spans.
- Columns may be offsets a maximum of 10% of the span (in direction o offset)from either axis between centre lines of successive columns.
- All loads shall be due to gravity only and uniformly distributed over entire panels. the live loads shall not exceed 2 times the dead load.
DOWNLOAD FLAT SLAB DESIGN EXAMPLE PDF
FOR PILE CAP AUTOCAD DRAWING -DOWNLOAD
TAG
flat slab design, flat slab reinforcement details, concrete slab roof design, column strip in flat slab, flat slab design example, column strip and middle strip in flat slab, flat slab design example is 456, design of flat slab by direct design method, two way flat slab, flat slab design as per is 456 pdf, flat slab design ppt, flat slab design pdf, flat slab details, flat slab maximum span, slab roof house design, flat slab span to depth ratio, flat plate construction, flat slab design example eurocode, slab roof plan, flat slab design nptel, equivalent frame method for flat slab, flat plate slab design, flat slab design example pdf, flat slab example, flat slab reinforcement details pdf, design of flat slab nptel, post tensioned flat slab design example, small house with slab roof, flat slab design calculation example, guide to the design and construction of reinforced ,concrete flat slabs, flat plate slab reinforcement details, flat slab roof design, design of interior panel of flat slab, guide to the design and construction of reinforced ,concrete flat slabs pdf, direct design method flat slab example, design and drawing of flat slab using is code method, flat plate reinforcement details, flat plate design example,












COMMENTS